Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
Tags
- 내부 클래스
- 객체지향
- 객체 지향
- 상속
- 제네릭
- 추상 클래스
- Encapsulation
- 캡슐화
- 추상화
- 와일드카드
- java
- 버퍼비우기
- python
- 17472
- enum
- 열거형
- 인터페이스
- 생성자
- this
- Final
- inheritance
- Scanner
- polymorphism
- 백준
- nextInt
- 다형성
- 프림알고리즘
- 최소신장트리
- abstract
Archives
- Today
- Total
쫑쫑이의 블로그
백준 9328 열쇠 Java [구현, BFS] 본문
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/9328
9328번: 열쇠
상근이는 1층 빌딩에 침입해 매우 중요한 문서를 훔쳐오려고 한다. 상근이가 가지고 있는 평면도에는 문서의 위치가 모두 나타나 있다. 빌딩의 문은 모두 잠겨있기 때문에, 문을 열려면 열쇠가
www.acmicpc.net

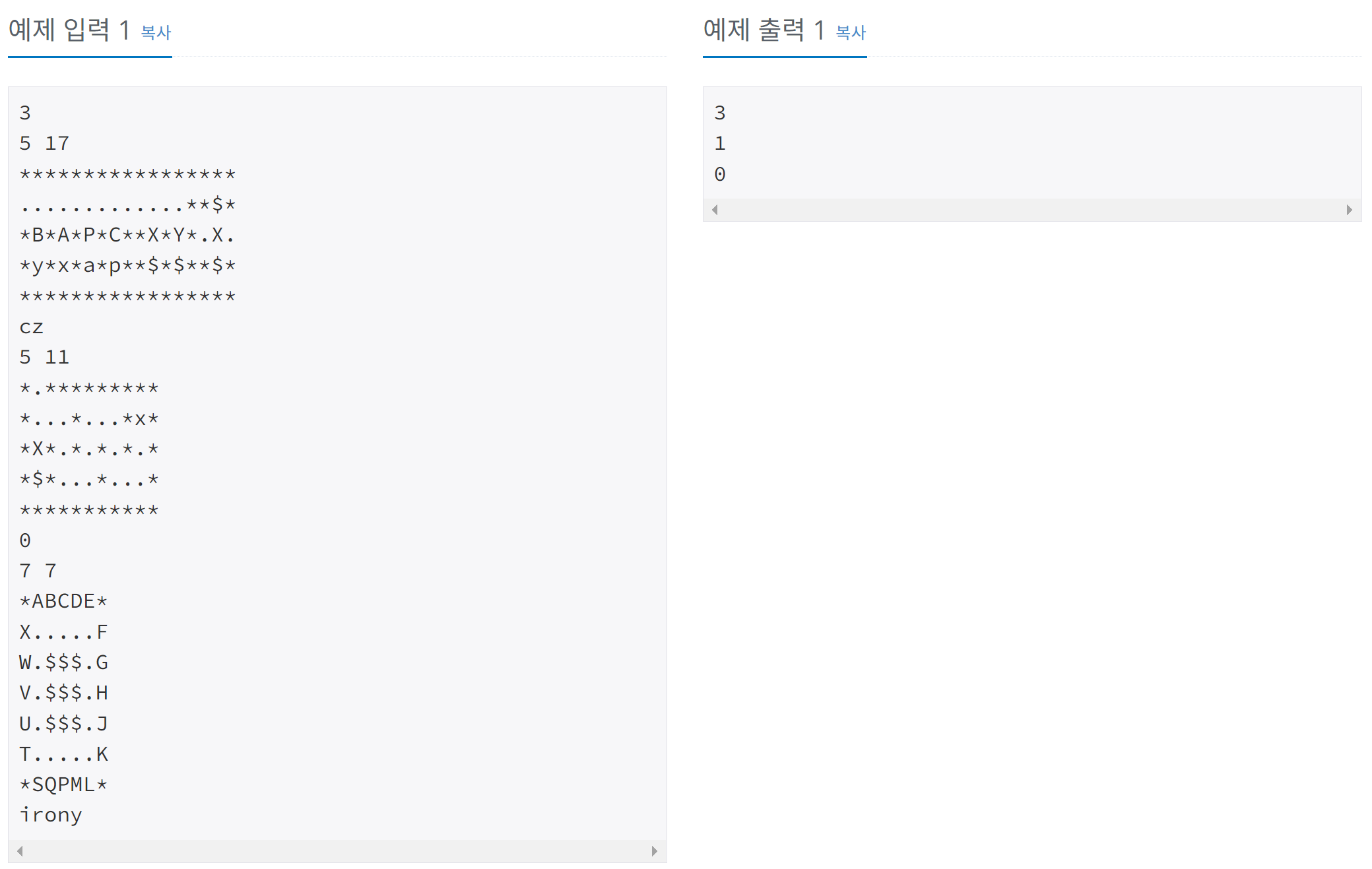
구현 문제이므로, 시키는대로 하면 된다!!!
문자를 전부 숫자로 바꿔서 배열을 만들었고,
마지막에 키를 받을 때 97씩 빼서 0 부터 26 사이의 가진 키들의 배열을 만들어줬다
42는 벽, 46은 빈 공간이다
모서리 순회하면서 조건에 만족하면 bfs로 탐색한다
42이거나 방문 했으면 리턴
1) 46이면 bfs 큐에 추가 (코드 내부에는 판별하는 조건문 없음)
2) 97보다 크면 키 추가하고 bfs 큐에 추가하고
2-1) Arraylist[]에서 반복문 돌리면서 큐에 넣고 new로 초기화
3) 65보다 크면 키 갖고있는지 확인
3-1) 없으면 키 Arraylist[]에 좌표 추가 후 리턴
3-2) 있으면 bfs 큐에 추가
4) 36이면 카운트하고 큐에 추가
공통되는 부분인 큐에 추가부분은 조건문 밖으로 꺼내줬다
import java.awt.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static final int KEY_LENGTH = 26;
static final int UPPERCASE = 65;
static final int LOWERCASE = 97;
static final int DOCS = 36;
static final int WALL = 42;
static BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static StringTokenizer st;
static Point[] dxy = new Point[]{new Point(1, 0), new Point(-1, 0), new Point(0, 1), new Point(0, -1)};
static Queue<Point> queue;
static int H, W, count;
static int[][] building;
static boolean[][] vtd;
static boolean[] keys;
static ArrayList<Point>[] doors;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int T = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int t = 0; t < T; t++) {
sb.append(test()).append("\n");
}
sb.setLength(sb.length() - 1);
System.out.println(sb);
}
static int test() throws IOException {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
H = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
W = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
building = new int[H][W];
vtd = new boolean[H][W];
keys = new boolean[KEY_LENGTH];
count = 0;
doors = new ArrayList[KEY_LENGTH];
for (int k = 0; k < KEY_LENGTH; k++) doors[k] = new ArrayList<>();
for (int h = 0; h < H; h++) {
building[h] = br.readLine().chars().toArray();
}
String str = br.readLine();
if (!str.equals("0")) str.chars().forEach(e -> keys[e-97] = true);
queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int w = 0; w < W - 1; w++) {
if (check(0, w)) search();
if (check(H - 1, W - w - 1)) search();
}
for (int h = 0; h < H - 1; h++) {
if (check(H - h - 1, 0)) search();
if (check(h, W - 1)) search();
}
return count;
}
static boolean check(int x, int y) {
int num = building[x][y];
if (num == WALL || vtd[x][y]) return false;
else if (num == DOCS) count++;
else if (num >= LOWERCASE) {
keys[num - LOWERCASE] = true;
for (Point p : doors[num - LOWERCASE]) {
queue.add(p);
}
doors[num - LOWERCASE] = new ArrayList<>();
}
else if (num >= UPPERCASE && !keys[num - UPPERCASE]) {
doors[num - UPPERCASE].add(new Point(x, y));
return false;
}
queue.add(new Point(x,y));
vtd[x][y] = true;
return true;
}
static void search() {
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Point now = queue.poll();
for (Point d : dxy) {
int nx = now.x + d.x;
int ny = now.y + d.y;
if (isInRange(nx, ny)) check(nx, ny);
}
}
}
static boolean isInRange(int x, int y) {
return (0 <= x && 0 <= y && x < H && y < W) ? true : false;
}
}
오랜만에 구현 문제를 풀었는데 고려해야할 사항들이 많고
잘했는지는 모르겠지만 기능 별로 나눠서 구조 짜는데 신경을 써서 꽤 시간이 걸렸다
코드 중복을 줄여서 재사용성을 높여보려했는데 static을 너무 많이 사용한 것 같다
'알고리즘 > 백준' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 7579 앱 Java [DP, 배낭문제] (0) | 2022.11.17 |
|---|---|
| 백준 2467 용액 Java [투포인터] (0) | 2022.11.16 |
| 백준 2252 줄 세우기 Java [위상정렬] (0) | 2022.11.14 |
| 백준 2239 스도쿠 Java [백트래킹, DFS] (0) | 2022.11.13 |
| 백준 1987 알파벳 Java [DFS] (0) | 2022.11.12 |




